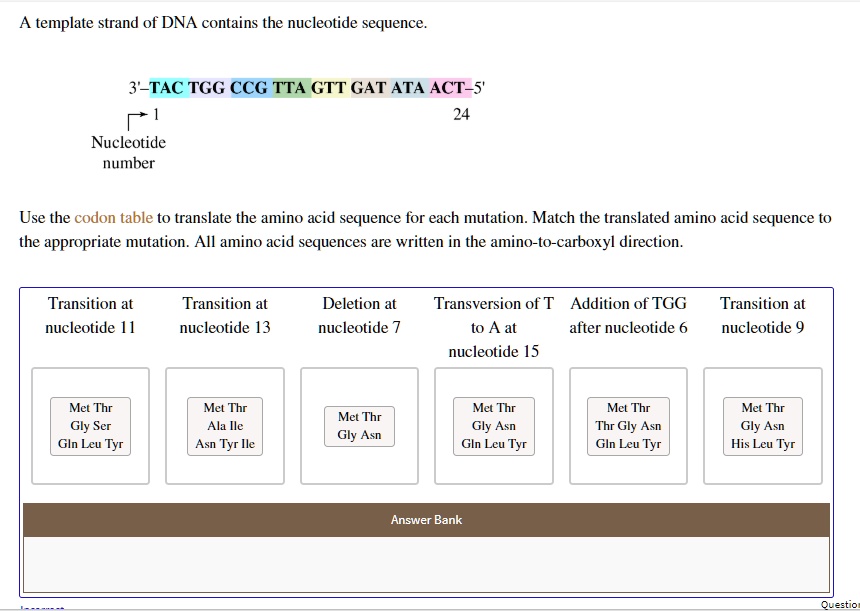
A Template Strand Of Dna Contains The Nucleotide Sequence
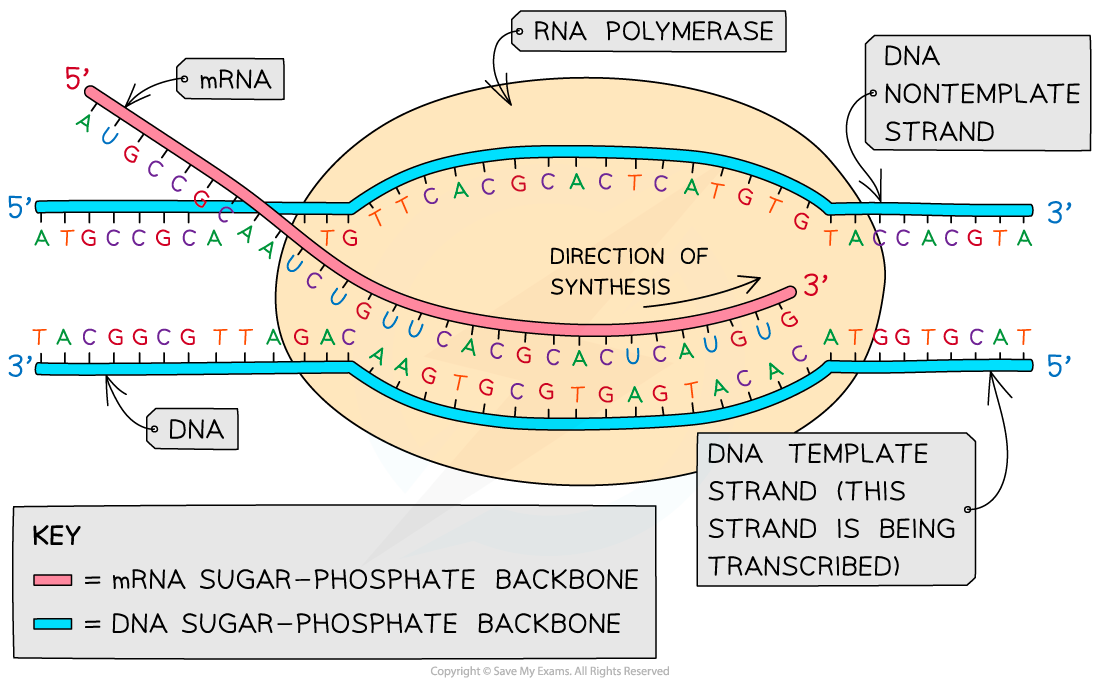
A Template Strand Of Dna Contains The Nucleotide Sequence - Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to each scenario. Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand in a sequence complementary to the template strand. Will match the sequence of the newly created rna strand except will contain the nucleotide uracil (u) in place of thymine (t) in dna The dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or. The dna template is used by rna polymerase to produce a strand of rna with a nucleotide sequence that is the same as the coding strand for the production of functional. Use the codon table to translate the amino acid sequence for each mutation. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. First, determine the amino acids of the protein encoded by this sequence by using the genetic code provided. Match the translated amino acid sequence to the appropriate mutation. The template strand serves as a. The following nucleotide sequence is found on the template strand of dna. The first nucleotide on the 3 prime end, t, is labeled nucleotide number 1 and the nucleotide on the 5 prime end, t, is labeled nucleotide number 24. Your solution’s ready to go! First, determine the amino acids of the protein encoded by this sequence by using the genetic code provided. The dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or. Match the translated amino acid sequence to the appropriate mutation. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to each scenario. Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Use the codon table to translate the. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. After the process of transcription, the mrna is converted into the mature. Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand in a sequence complementary to the template strand. Use the codon table to translate the amino acid sequence for each mutation.. During transcription, the process of creating rna, one of the two strands of dna acts as a template, providing the instructions for the arrangement of nucleotides in the rna. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what role does dna play in the cell?, select all of the bases that can be present in dna nucleotides., a dna. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. Serves as the blueprint for mrna formation, guiding its synthesis. The dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or. Use the sequence to determine the type. It requires a primer, a short rna. The following nucleotide sequence is found on the template strand of dna. During transcription, the process of creating rna, one of the two strands of dna acts as a template, providing the instructions for the arrangement of nucleotides in the rna. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to. Serves as the blueprint for mrna formation, guiding its synthesis. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. The dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence). Will match the sequence of the newly created rna strand except will contain the nucleotide uracil (u) in place of thymine (t) in dna During transcription, the process of creating rna, one of the two strands of dna acts as a template, providing the instructions for the arrangement of nucleotides in the rna. First, determine the amino acids of the. Determines the accurate nucleotide sequence for the resultant. Use the codon table to translate the. Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand in a sequence complementary to the template strand. Serves as the blueprint for mrna formation, guiding its synthesis. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to each scenario. Your solution’s ready to go! The dna template is used by rna polymerase to produce a strand of rna with a nucleotide sequence that is the same as the coding strand for the production of functional. The term template strand. The dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or. It requires a primer, a short rna. Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand in a sequence complementary to the template strand. Will match the. Determines the accurate nucleotide sequence for the resultant. The dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or. The first nucleotide on the 3 prime end, t, is labeled nucleotide number 1 and the nucleotide on the 5 prime end, t, is. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. Use the codon table to translate the amino acid sequence for each mutation. The first nucleotide on the 3 prime end, t, is labeled nucleotide number 1 and the nucleotide on the 5 prime end, t, is labeled nucleotide number 24. The dna template is used by rna polymerase to produce a strand of rna with a nucleotide sequence that is the same as the coding strand for the production of functional. After the process of transcription, the mrna is converted into the mature. Use the sequence to determine the type of mutation and the type of base substitutions that apply to each scenario. The dna sequence that is transcribed to make rna is called the template strand, while the complementary sequence on the other dna strand is called the coding or. It requires a primer, a short rna. The following nucleotide sequence is found on the template strand of dna. The given dna non‑template sequence (coding sequence) is transcribed from 5' to 3'. Determines the accurate nucleotide sequence for the resultant. During transcription, the process of creating rna, one of the two strands of dna acts as a template, providing the instructions for the arrangement of nucleotides in the rna. Your solution’s ready to go! A template strand of dna contains the nucleotide sequence. Use the codon table to translate the. Match the translated amino acid sequence to the appropriate mutation.DNA Replication · Concepts of Biology
6 Illustration of a nucleotide and a DNA strand. Download Scientific
DNA sequencing Britannica
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
SOLVED template strand of DNA contains the nucleotide sequence. 3TAC
5.4 DNA Replication Human Biology
The Structure of DNA by Ron Vale
DNA structure.DNA with its components cytosine,guanine,adenine
CIE A Level Biology复习笔记6.2.4 Transcription翰林国际教育
Original Template Dna Strand
Serves As The Blueprint For Mrna Formation, Guiding Its Synthesis.
First, Determine The Amino Acids Of The Protein Encoded By This Sequence By Using The Genetic Code Provided.
The Template Strand Serves As A.
Dna Polymerase Plays A Pivotal Role By Adding Nucleotides To The Growing Dna Strand In A Sequence Complementary To The Template Strand.
Related Post: