Dna Coding Strand Vs Template Strand
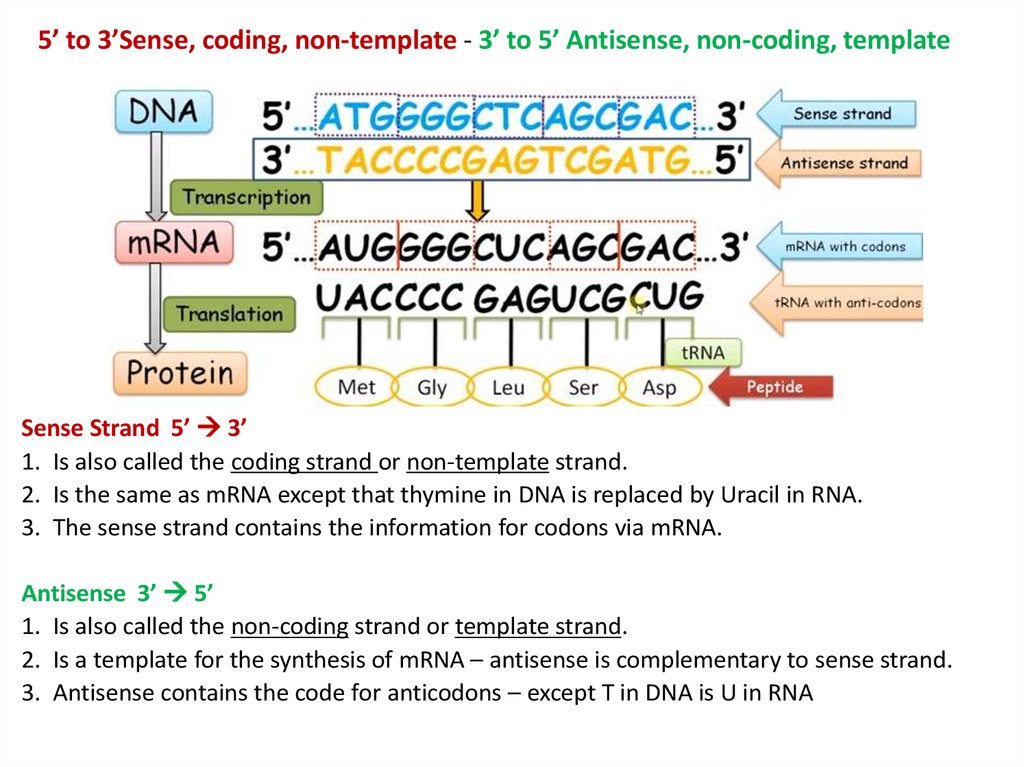
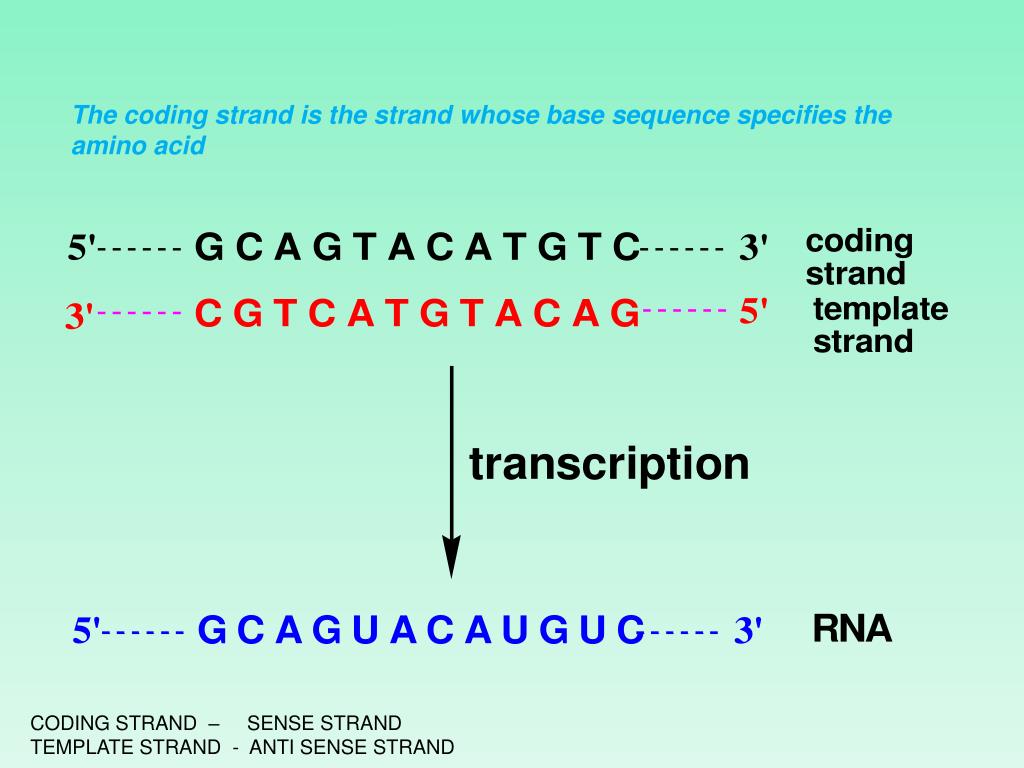
Dna Coding Strand Vs Template Strand - The template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template during transcription, allowing the synthesis of rna molecules that are. The template strand serves as a. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? Dna’s intricate design includes two fundamental strands: One strand is actively used as a template strand in the transcription process. The coding strand provides the template for the synthesis of proteins, while the template strand provides the template for the synthesis of a new dna strand during replication. The coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. Transcription is the synthesis of a. On the other hand, the. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. Dna’s intricate design includes two fundamental strands: Two of its key components are the coding strand and the template strand, each with its unique properties and functions. On the other hand, the. The coding strand provides the template for the synthesis of proteins, while the template strand provides the template for the synthesis of a new dna strand during replication. The coding strand of the dna has a base sequence. The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the production of rna, whereas the coding strand is the other strand. The coding strand and the template strand. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna. Generally, dna consists of two complementary strands, the coding strand and the template strand. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? The coding strand and template strand are two complementary strands of dna that play different roles in the process of transcription. The template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template during transcription,. Generally, dna consists of two complementary strands, the coding strand and the template strand. The coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. The coding strand and the template strand. Imagine these as partners in a genetic dance. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. Imagine these as partners in a genetic dance. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same. The coding strand of. Generally, dna consists of two complementary strands, the coding strand and the template strand. The coding strand of the dna has a base sequence. Two of its key components are the coding strand and the template strand, each with its unique properties and functions. One strand is actively used as a template strand in the transcription process. The coding strand. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same. Dna’s intricate design includes two fundamental strands: Understanding the distinction between the coding strand and template strand is essential in comprehending the complex processes of dna replication and gene expression. One strand is actively used as a template strand in the transcription process. The coding strand of dna. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. The template strand serves as a. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. On the other hand, the. The dna strand known as the template. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. On the other hand, the. The coding strand of the dna has a base sequence. The coding strand, also known as the sense strand, is the dna strand that has the. The coding strand provides the template for the. The coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. One strand is actively used as a template strand in the transcription process. The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the production of rna, whereas the coding strand is the other strand. In the. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. Generally, dna consists of two complementary strands, the coding strand and the template strand. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. The coding strand of the dna has a base sequence. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. Generally, dna consists of two complementary strands, the. These strands play a vital role in the process of gene expression and protein synthesis. The coding strand of the dna has a base sequence. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna. On the other hand, the. This strand is known as the sense strand or template strand. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. The coding strand has the same sequence as the rna transcript and acts as. Understanding the distinction between the coding strand and template strand is essential in comprehending the complex processes of dna replication and gene expression. The coding strand is the strand of dna that has the same. Transcription is the synthesis of a. Generally, dna consists of two complementary strands, the coding strand and the template strand. Dna’s intricate design includes two fundamental strands: Two of its key components are the coding strand and the template strand, each with its unique properties and functions. One strand is actively used as a template strand in the transcription process. The coding strand, also known as the sense strand, is the dna strand that has the. Imagine these as partners in a genetic dance.Dna Coding And Template Strands
Coding vs. Template DNA Strands The Key Differences Explained Blog
Template Strand Vs Coding Strand Understanding The Difference GRAPHICOLD
DNA Coding Strand Vs Template Strand Ppt Powerpoint Images Cpb
Template And Non Template Strand Of Dna
Coding Strand And Template Strand
Coding Vs Template Strand, Web dna’s vital role in biology.
Understanding DNA Coding Strand vs Template Strand Explained
Coding vs. Template DNA Strands The Key Differences Explained Blog
Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
What Is The Difference Between Coding Strand And Template Strand?
The Coding Strand Of Dna Is The Strand That Codes For The Gene Of Interest.
The Template Strand Serves As A.
The Coding Strand Provides The Template For The Synthesis Of Proteins, While The Template Strand Provides The Template For The Synthesis Of A New Dna Strand During Replication.
Related Post: