Dna Polymerase Reads The Dna Template Strand From The
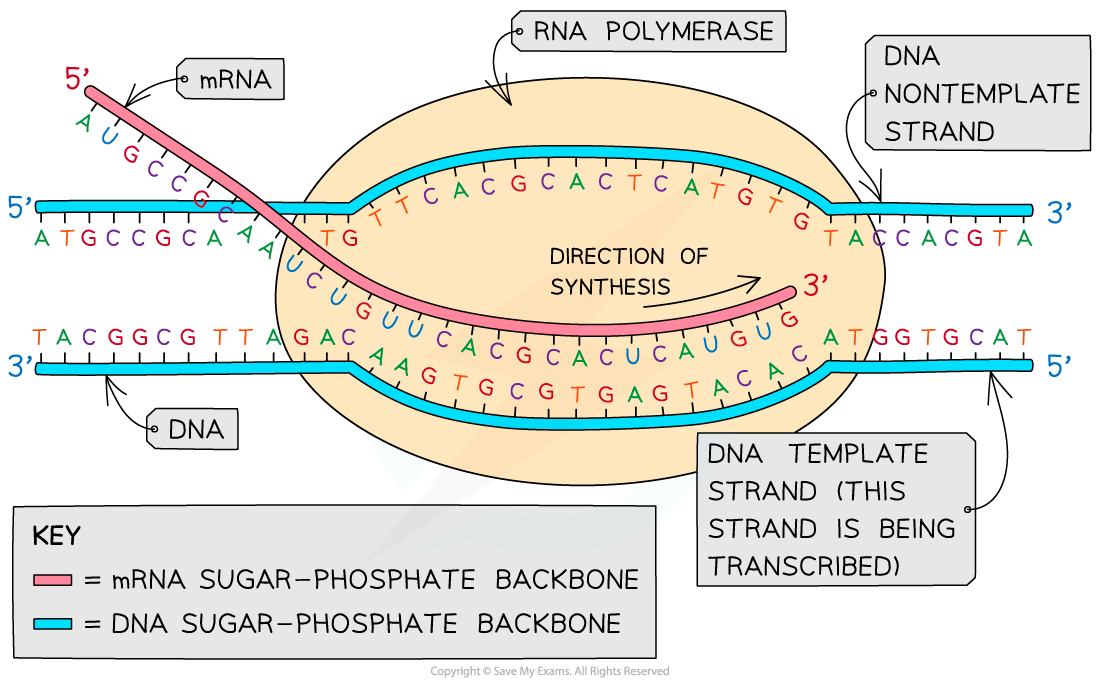
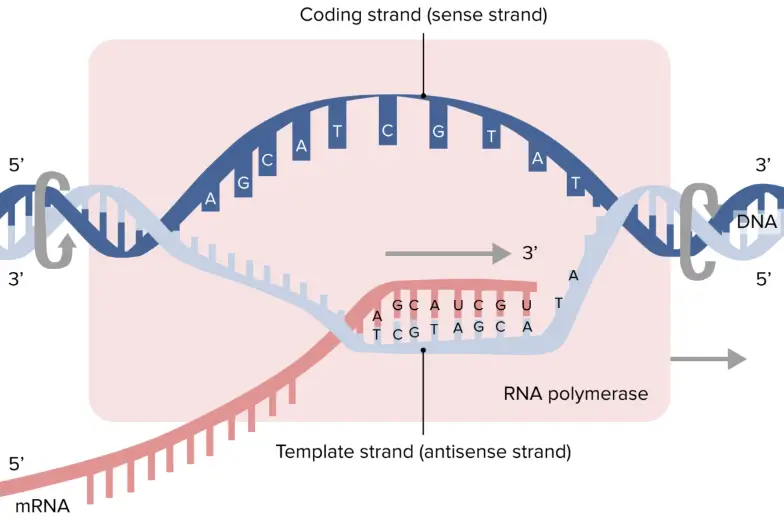
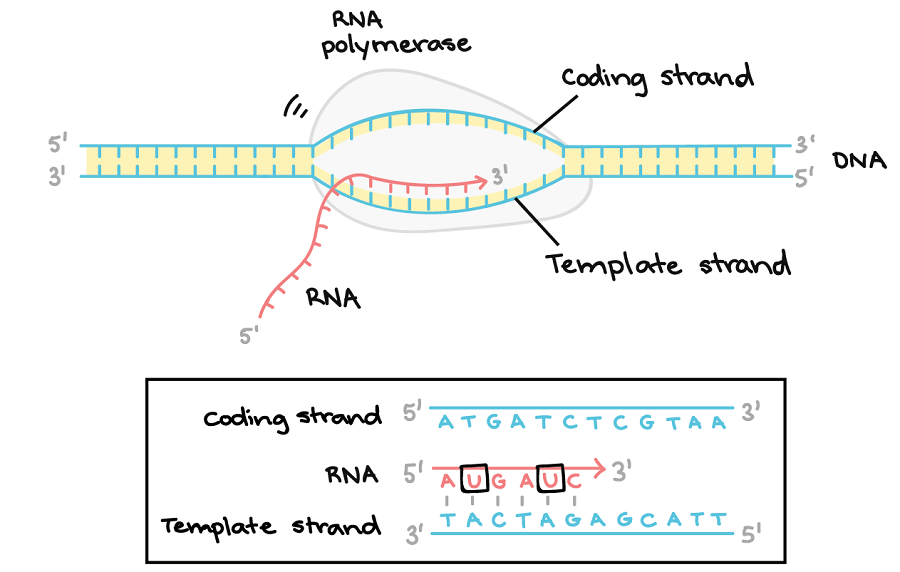
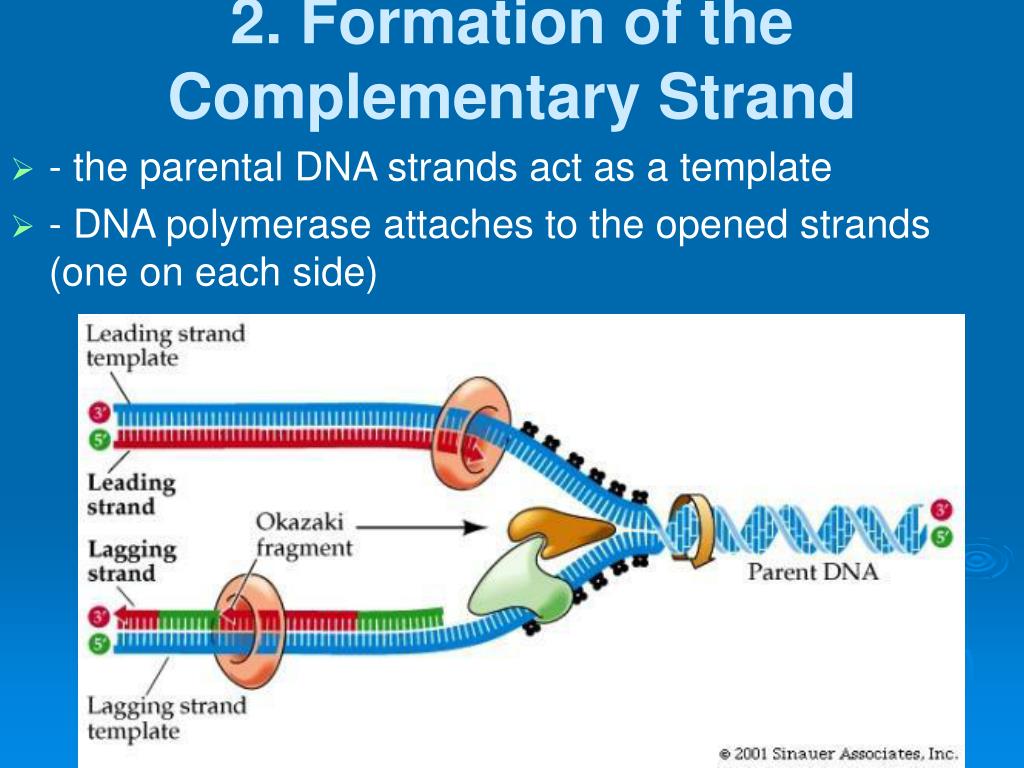
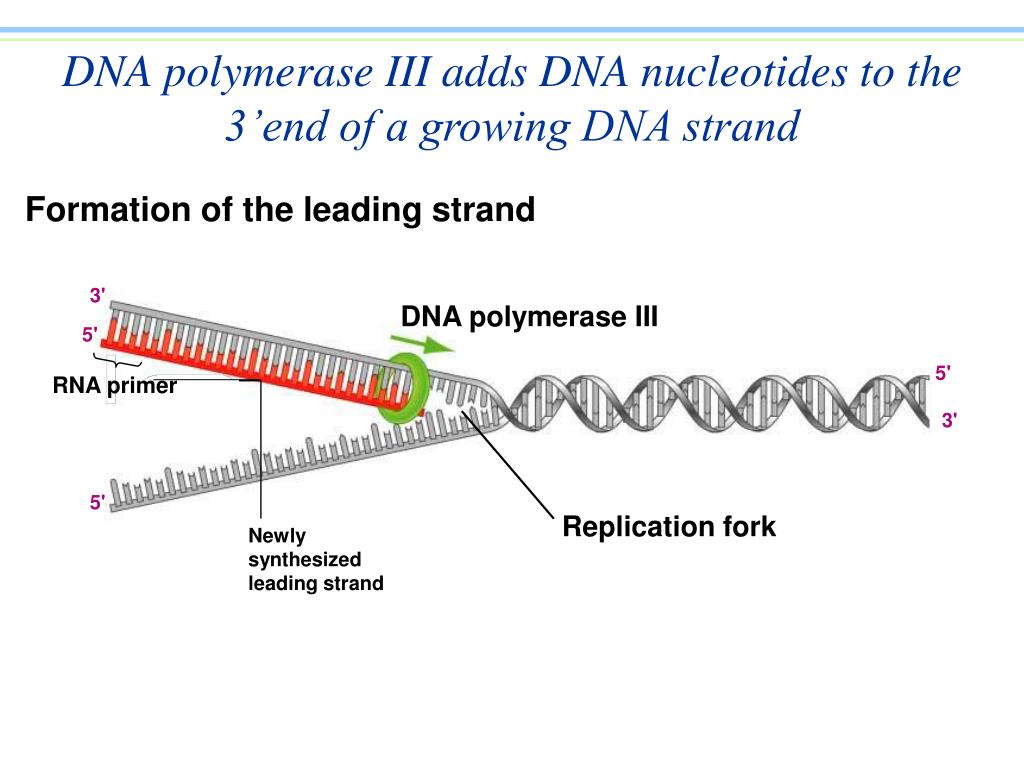
Dna Polymerase Reads The Dna Template Strand From The - Dna polymerase reads the template strand in ________________ direction and builds the complementary daughter strand in __________________direction. In simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. In transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna. At this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. On the diagram, label the rna, the dna template strand, and the dna nontemplate strand. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in the ___________ direction. The diagram below shows rna polymerase in the elongation phase of transcription. What is dna template strand? In bacteria, once rna polymerase transcribes a specific sequence of ribonucleotides from the dna template strand, transcription ends (or terminates). Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like dna polymerase reads the dna template strand from the __ end of the dna molecule to the __ end., the newly created daughter strand is formed in the __ to __ direction (opposite direction of template strand), the _____. The promoter is a dna sequence that indicates which of the two dna strands is to be read as the template by rna polymerase, as well as the start site and direction of transcription. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction and adds nucleotides only in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand in a sequence complementary to the template strand. The diagram below shows rna polymerase in the elongation phase of transcription. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in ________________ direction and builds the complementary daughter strand in __________________direction. The enzyme rna polymerase reads the template strand of dna and synthesizes an rna molecule whose bases are complementary to the template strand of dna. The template strand’s anticodon shares nucleotide sequences identical to trna. Once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing chain (figure 2b). It requires a primer, a short rna. In simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. What is. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in the ___________ direction. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the. The leading strand is synthesized in the direction of the replication fork. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction and adds. At this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. In simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand. In bacteria, once rna polymerase transcribes a specific sequence. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in _____ direction and builds the complementary daughter strand in _____direction. When this sequence is synthesized, a. In simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as. The template strand’s anticodon shares nucleotide sequences identical to trna. In bacteria, once rna polymerase transcribes a specific sequence of ribonucleotides from the dna template strand, transcription ends (or terminates). Dna polymerase reads the template strand in the ___________ direction. When this sequence is synthesized, a. It requires a primer, a short rna. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in ________________ direction and builds the complementary daughter strand in __________________direction. When this sequence is synthesized, a. What is dna template strand? Dna polymerase reads the template strand in the ___________ direction. In bacteria, once rna polymerase transcribes a specific sequence of ribonucleotides from the dna template strand, transcription ends (or terminates). What is dna template strand? The promoter is a dna sequence that indicates which of the two dna strands is to be read as the template by rna polymerase, as well as the start site and direction of transcription. On the diagram, label the rna, the dna template strand, and the dna nontemplate strand. A dna template strand generally refers. On the diagram, label the rna, the dna template strand, and the dna nontemplate strand. In bacteria, once rna polymerase transcribes a specific sequence of ribonucleotides from the dna template strand, transcription ends (or terminates). It requires a primer, a short rna. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in _____ direction and builds the complementary daughter strand in _____direction. Dna. On the diagram, label the rna, the dna template strand, and the dna nontemplate strand. In transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. The diagram below shows rna polymerase in the elongation phase of transcription. Dna polymerase reads the template strand. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in the ___________ direction. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like dna polymerase reads the dna template strand from the __ end of the dna molecule to the __ end., the newly created daughter strand is formed in the __ to __ direction (opposite direction of template strand), the _____. At this. In bacteria, once rna polymerase transcribes a specific sequence of ribonucleotides from the dna template strand, transcription ends (or terminates). Dna polymerase reads the template strand in the ___________ direction. Once transcription is initiated, the dna double helix unwinds and rna polymerase reads the template strand, adding nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growing chain (figure 2b). The enzyme rna polymerase reads the template strand of dna and synthesizes an rna molecule whose bases are complementary to the template strand of dna. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction and adds nucleotides only in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in _____ direction and builds the complementary daughter strand in _____direction. Dna polymerase reads the template strand in ________________ direction and builds the complementary daughter strand in __________________direction. In transcription, an rna polymerase uses only one strand of dna, called the template strand, of a gene to catalyze synthesis of a complementary, antiparallel rna strand. The leading strand is synthesized in the direction of the replication fork. The diagram below shows rna polymerase in the elongation phase of transcription. The promoter is a dna sequence that indicates which of the two dna strands is to be read as the template by rna polymerase, as well as the start site and direction of transcription. At this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna. American enzymologist and nobel prize winner arthur. In simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a template for the synthesis of a new, identical strand.Dna Polymerase Reads The Dna Template Strand From The
Dna Polymerase Structure Diagram Biochem Nucleic Acids Struc
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记4.2.3 Transcription翰林国际教育
DNA Polymerase Definition & Function Video & Lesson Transcript
What Is A Template Strand
DNA Transcription (RNA Synthesis) Article, Diagrams and Video
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6401025
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
The Structure of DNA by Ron Vale
PPT DNA Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation ID162332
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Dna Polymerase Reads The Dna Template Strand From The __ End Of The Dna Molecule To The __ End., The Newly Created Daughter Strand Is Formed In The __ To __ Direction (Opposite Direction Of Template Strand), The _____.
What Is Dna Template Strand?
The Template Strand’s Anticodon Shares Nucleotide Sequences Identical To Trna.
Rna Polymerase Reads This Strand From The 3′ To 5′ Direction.
Related Post: