Is The Template Strand Always 3 To 5
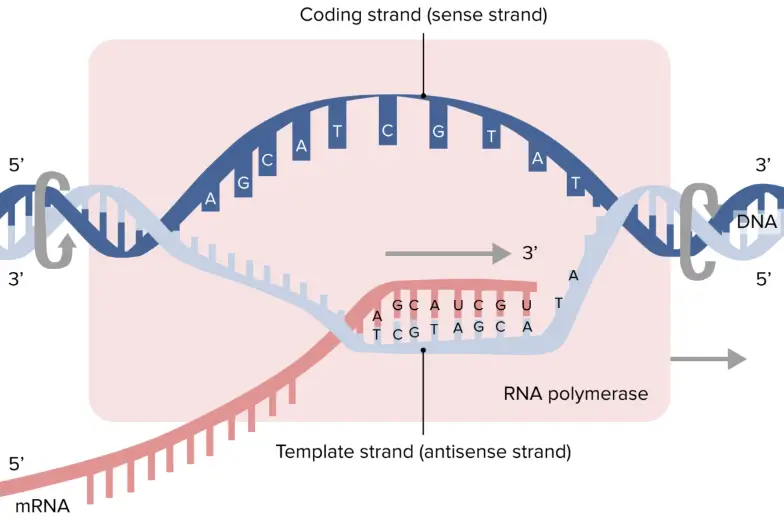
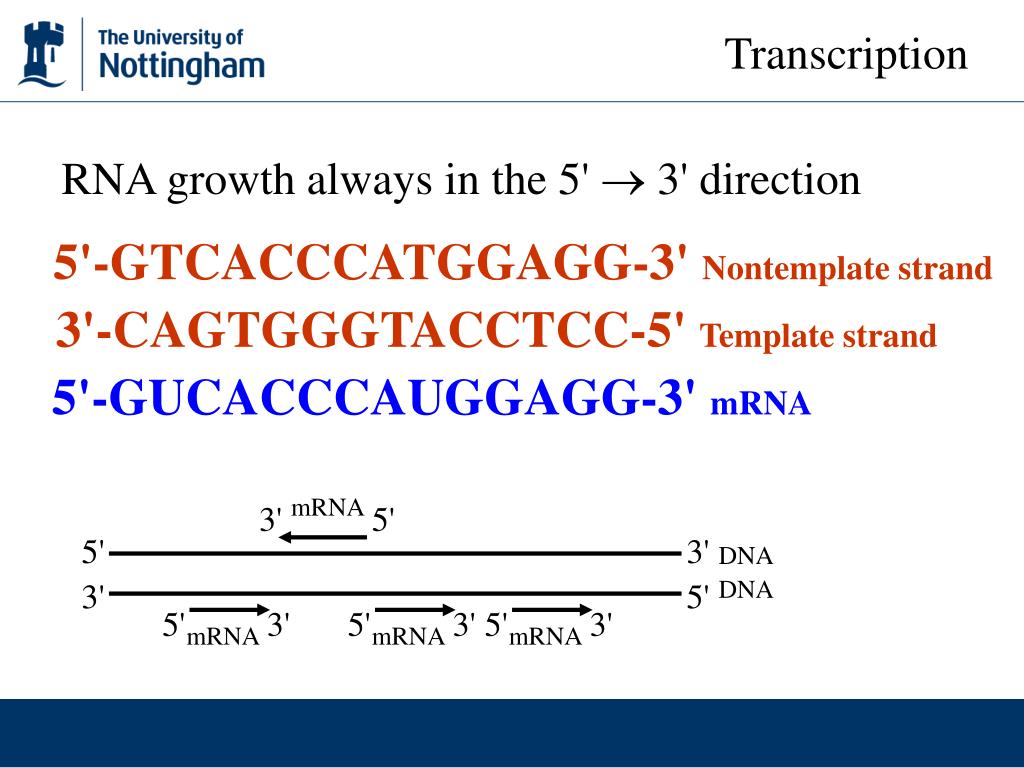
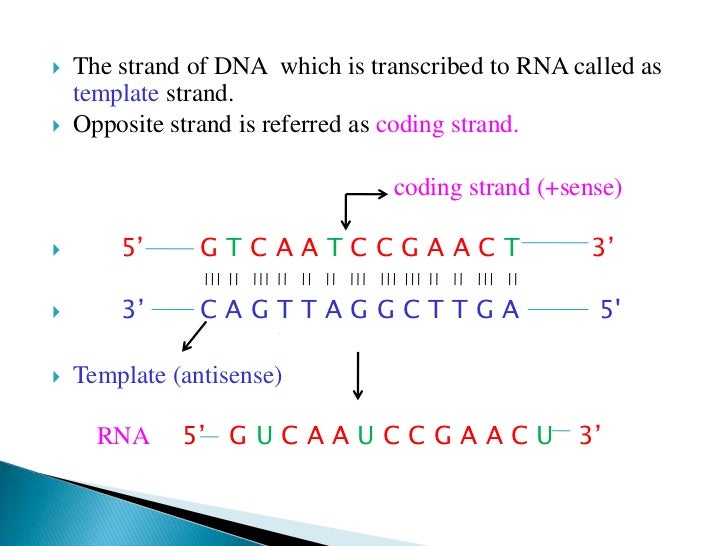
Is The Template Strand Always 3 To 5 - Nucleotides pair with complementary bases on the dna. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. It lays down its nucleic acids in the 5' to 3' direction. In order to make the other strand it adds nucleotides in the 3’ end. The dna strand that is used for synthesis is known. Dna poly reads the template strand in the 3' to 5' direction. Is the 5 to 3 strand the template strand? For example, if the top strand is from 5’ to 3’, the polymerase simply. Any of the strands can become template strand. One strand is the coding strand, which has the same sequence as the mrna (except for the substitution of u for t), and the other is the template strand, which is read by rna polymerase. This is because dna polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes new dna, can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of. For example, if the top strand is from 5’ to 3’, the polymerase simply. Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. Rna polymerase moves along the template strand in a 3′ to 5′ direction, assembling rna nucleotides in a 5′ to 3′ direction. Yes, the template strand of dna is oriented in the 3' to 5' direction. Template strand contains the complementary. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the. Template strand which is also known as antisense strands runs in the direction of 3’ to 5’ ends, which runs opposite to the coding strands. The template strand, being used as a literal template, is also known as the non. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. The template strand, being used as a literal template, is also known as the non. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus strand, plays an important role in rna synthesis. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna synthesis. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. During elongation,. Template strand contains the complementary. The coding strand has a complementary nucleotide sequence. In order to make the other strand it adds nucleotides in the 3’ end. The template strand, being used as a literal template, is also known as the non. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. The template strand, being used as a literal template, is also known as the non. Any of the strands can become template strand. During elongation, rna polymerase “walks” along one strand of dna, known as the template strand, in the 3′ to 5′ direction. Nucleotides pair with complementary bases on the dna. The template strand is directed in the 5’. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to synthesize a. During elongation, rna polymerase “walks” along one strand of dna, known as the template strand, in the 3′ to 5′ direction. The coding strand, also called the sense. Rna polymerase moves along the template strand in a 3′ to 5′ direction, assembling rna nucleotides in a 5′ to 3′ direction. One strand is the coding strand, which has the same sequence as the mrna (except for the substitution of u for t), and the other is the template strand, which is read by rna polymerase. Dna poly reads. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. During elongation, rna polymerase “walks” along one strand of dna, known as the template strand, in the 3′ to 5′ direction. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to synthesize a. It lays down its nucleic acids in the 5' to 3'. As the polymerase elongates the nascent rna strand at its 3' end, it moves towards the 5' end of the dna strand it is using as a template. Alternatively both strand work as template strand. Dna poly reads the template strand in the 3' to 5' direction. This is because dna polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes new dna, can only. This is because dna polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes new dna, can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of. The template strand, being used as a literal template, is also known as the non. It’s read by rna polymerase in the 3′ to 5′ direction, allowing the enzyme to synthesize a. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule,. Nucleotides pair with complementary bases on the dna. The dna strand that is used for synthesis is known. The template strand, or antisense strand, serves as the blueprint for rna synthesis. The template strand, being used as a literal template, is also known as the non. During elongation, rna polymerase “walks” along one strand of dna, known as the template. The dna strand that is used for synthesis is known. It lays down its nucleic acids in the 5' to 3' direction. Dna polymerase reads from the 3’ to 5’ in one strand. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Dna poly reads the template strand in the 3' to 5' direction. Rna polymerase moves along the template strand in a 3′ to 5′ direction, assembling rna nucleotides in a 5′ to 3′ direction. The coding strand is directed in the 3’ to 5’ direction. One strand is the coding strand, which has the same sequence as the mrna (except for the substitution of u for t), and the other is the template strand, which is read by rna polymerase. For example, if the top strand is from 5’ to 3’, the polymerase simply. Template strand contains the complementary. This is because dna polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes new dna, can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of. Template strand which is also known as antisense strands runs in the direction of 3’ to 5’ ends, which runs opposite to the coding strands. Is the 5 to 3 strand the template strand? Template strand functions as a base for the rna synthesis. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Alternatively both strand work as template strand. The dna strand that is used for synthesis is known. The template strand, being used as a literal template, is also known as the non. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. The coding strand functions to determine the correct nucleotide base sequence of the rna strand.What Is A Template Strand
PPT Transcription in Prokaryotes PowerPoint Presentation, free
[Solved] During DNA replication, how does each template strand
Dna Coding And Template Strands
Solved Create a 3' to 5' template strand from the 5' to 3'
What Is The Template Strand
Difference Between Coding Strand And Template Strand
What Is The Template Strand, The template strand acts as a base for
Key Components Of Gene Transcription Diagram Transcription D
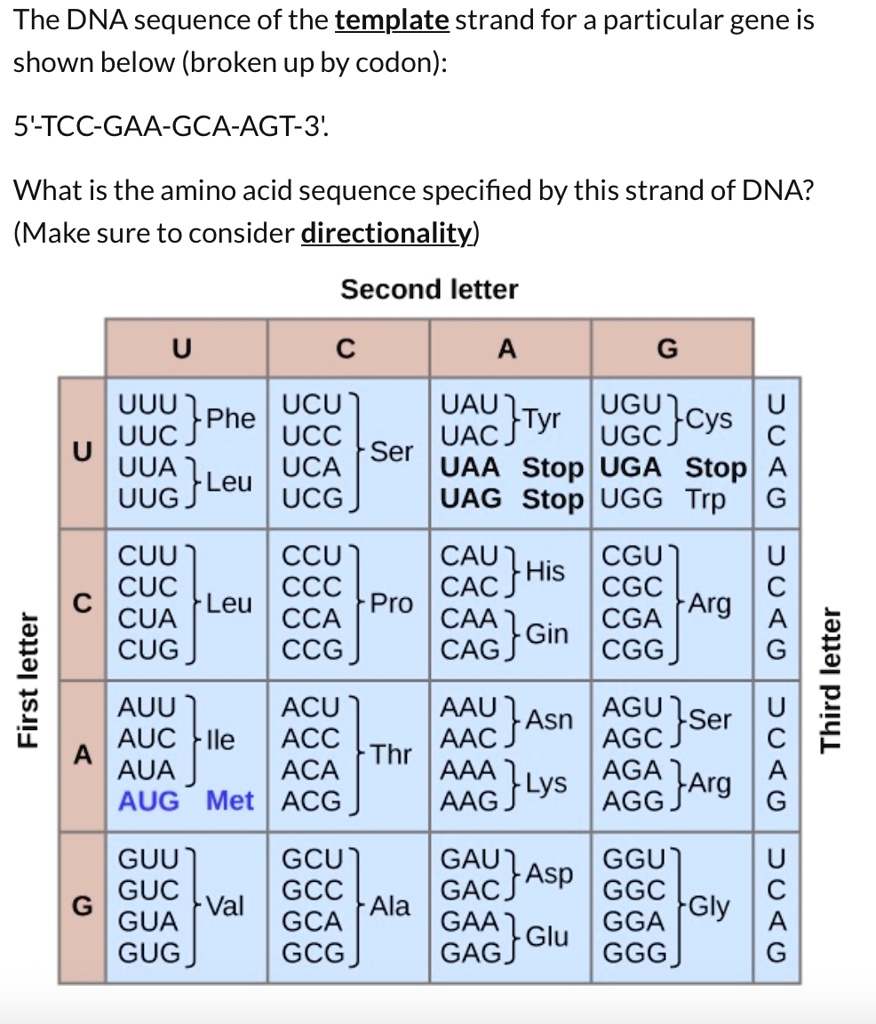
SOLVED The DNA sequence of the template strand for a particular gene
Yes, A Template Dna Strand Is Always Oriented 3' To 5' Because Mrna Is Synthesized In The 5′ To 3′ Direction And Mrna And Template Dna Have To Be Antiparallel In Order For Mrna To Have.
Dna Polymerase Reads From The 3’ To 5’ In One Strand.
The Template Strand, Also Referred To As The Antisense Strand Or The Minus Strand, Plays An Important Role In Rna Synthesis.
So Basically Coding V Template And.
Related Post: